Carbon Management (CM)
As a pioneer for professional carbon management on the way to achieving genuine climate neutrality, the University of Graz is a strong research and implementation partner in climate action, both through its transparent greenhouse gas accounting and through innovative research and knowledge transfer. As a new solution framework, the Carbon Management (CM) approach offers research-based knowledge, innovative tools and services for those responsible at all levels (policymakers, organizations, companies, individuals) to manage greenhouse gas reduction measures in accordance with the Paris Climate Agreement.
How also your organization can become climate neutral
With the Carbon Management (CM) approach, we can also lead your organization or company to a genuine climate neutrality. If you aim to become climate neutral in the face of the climate crisis, you can rely on a strong partner with the Carbon Management Partners Team of the University of Graz (contact: CM Dissemination Partners). Together with you, the dissemination partners will design a successful climate target path and action framework to make your organization reliably “climate fit”. Our solution approach ensures that you will reach genuine climate neutrality and thus a fair share and contribution to the achievement of the Paris climate goals. Your long-term strategy towards climate neutrality is based on your previous greenhouse gas emissions, which we compute for you and from which you start your climate target path.
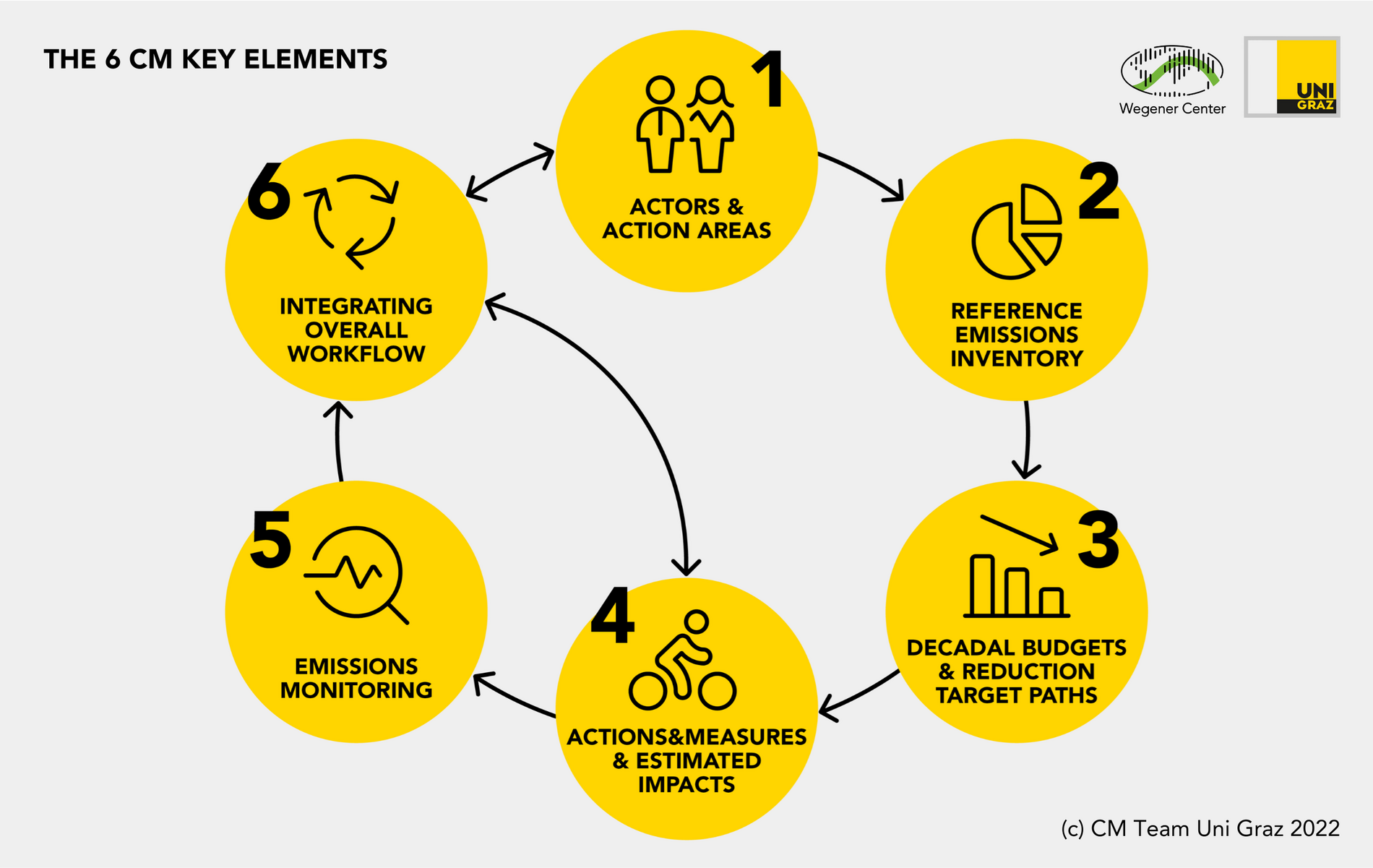
Step 1: Define actors and action areas
As a basic framework for the carbon management and to enable successful emission reductions, the relevant actors as well as areas of action in an organization are clearly defined.
Step 2: Compute a reference emissions Iinventory
The greenhouse gas emissions of recent years prior to 2020 are computed to obtain base-year emissions for the action areas; these “Reference Emissions 2020” are the starting base for reductions.
Step 3: Adopt decadal budgets and reduction target paths
Maximum decadal emission budgets and embedded year-by-year reduction target paths are adopted for the 2020s and 2030s, which correspond to a fair share to reaching the Paris climate goals.
Step 4: Prepare actions and measures and quantify their estimated impacts
As a crucial step towards implementation, concrete measures to achieve the targets are defined in all action areas and their estimated impacts in terms of contributed reduction rates are quantified.
Step 5: Set up and carry out emissions monitoring
For tracking the progress of implementation, an emissions monitoring is set up and carried out, providing a solid quantitative basis and guidance for further improved measures as needed.
Step 6: Implement an integrating overall workflow
A dynamic decision support workflow connects and integrates the steps of the carbon management and supports continual improvements towards achieving the targets.
What is the difference between net-zero emissions and climate neutrality?
Carbon Management (CM) uses a two-steps definition of “net-zero” and “climate neutral”, to ensure a genuine (honest) climate neutrality. As an important innovation to existing baseline definitions (see, e.g., KUH, OOP, SBTi), this helps to safeguard carbon managing organizations from the risk of “greenwashing” through overemphasizing purchases of greenhouse gas (GHG) removal from the atmosphere compared to their own emission reductions. In this way it helps to ensure the fairness of their contribution towards achieving the Paris climate goals.
According to the CM Standard, the goal of Net-zero in the GHG net emissions of a year is achieved if the GHG amount removed from the atmosphere equals the remaining emissions amount, whereby the removal should be done sustainably such as through nature-based carbon storage. For reaching the current reduction targets of the University of Graz, for example, at least 68% of the reference emissions amount must be reduced by 2030 and at the same time up to 32% removal share must be built up in order to achieve net-zero emissions.
The goal Climate neutral is only achieved by an organization when it has already been able to reduce at least 90% of its (consumption-based) GHG reference emissions. Hence it can and must balance a maximum of 10% of remaining emissions through GHG removals, consistent with the limited global availability of sustainable carbon storage and thus a fair removal share in a climate neutral world.
The table below summarizes this CM two-steps definition in a technically more accurate formulation.
Net-zero
Sum of the percentages of GHG emission reduction and GHG removal from the atmosphere relative to the GHG amount of the reference emissions inventory [tCO2eq] (RefEms2020, start of target paths) equals 100(±5)% in a future year (e.g., 2030), whereby the emission reduction contributes less than 90%.
Source reference (if citing this Intro website):
[Kirchengast et al., 2024] Kirchengast, G., J. Danzer, and S. Hölbling (2024): Carbon Management (CM) – The successful path to climate neutrality. CM Short Introduction Online: https://wegcenter.uni-graz.at/en/carbon-management (last access DD Month 202Y).
>> More information on CarbManage.Earth